Why Does Digital Transformation Matter In Supply Chain Management?
Digitization in supply chain management empowers your planning, sourcing, and logistics teams to collaborate, automate and effectively leverage analytics. It has also proven to drive growth, mitigate risk, and optimize costs. 
Traditional vs. Digital Supply Chains
Traditional supply chains function on rules based on historical transactional inputs, while supply chains integrated with digital technologies function in real-time. While digital supply chains are networks, traditional supply chains are linear.
In digital supply chain management, information from IT and operational technology systems are integrated, while traditional supply chains often rely on standalone systems. Traditional supply chains require a lot of legwork when it comes to spotting possible problems and predicting likely risks. In such situations, an IT consulting company has a great role to play.
It’s important to note that digital supply chains are not necessarily a complete replacement for traditional supply chains. In many cases, a hybrid approach that combines digital and traditional elements may be the most effective solution, depending on the specific industry, company, and supply chain requirements.
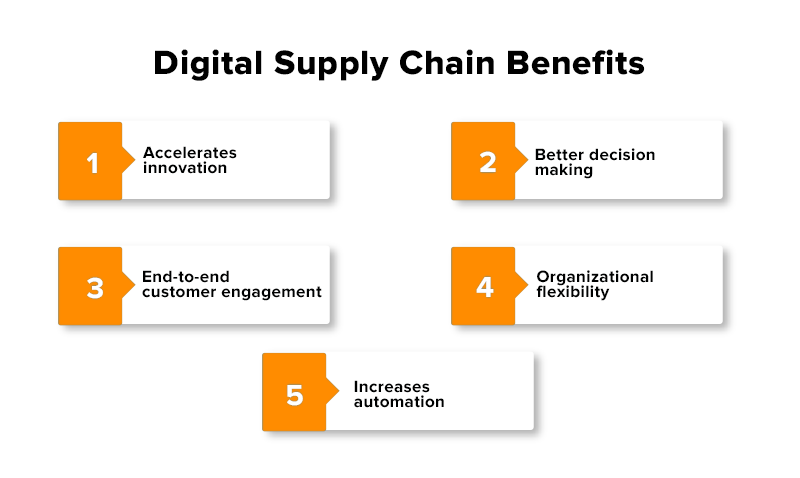
Benefits of Digital Supply Chains:
Digital supply chains offer several advantages over traditional supply chains, including:
Improved Efficiency: Automation, digitization, and streamlined processes result in faster order fulfillment, reduced lead times, and improved productivity.
Enhanced Visibility: Real-time data and analytics provide better visibility into supply chain operations, enabling proactive decision-making and faster problem resolution.
Greater Flexibility: Digital supply chains are more adaptable to market changes, allowing for quicker responses to demand fluctuations or disruptions in the supply network.
Enhanced Collaboration: Digital platforms enable better communication and collaboration among supply chain partners, leading to improved coordination and synchronization of activities.
Cost Savings: Digital supply chains can reduce costs by eliminating manual processes, optimizing inventory levels, minimizing stockouts, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Digital tools, automation, and data analytics to optimize various supply chain processes.

Tech Trends In Supply Chain Digital Transformation
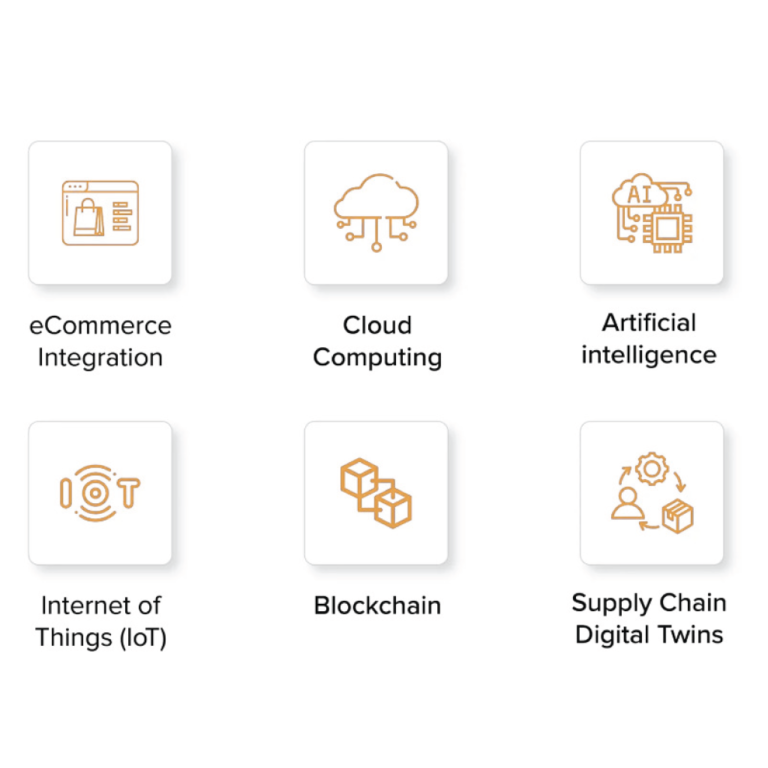
Supply chain digital transformation is driven by advancements in technology that enable organizations to optimize their supply chain operations and gain a competitive edge.
Here are some of the top tech trends in supply chain digital transformation:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data. In the supply chain, IoT enables real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, assets, and inventory. It enhances visibility, enables proactive maintenance, improves asset utilization, and supports predictive analytics.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies are revolutionizing supply chain operations. They can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, optimize processes, and make data-driven predictions. AI-powered algorithms can optimize demand forecasting, improve inventory management, automate routine tasks, optimize route planning, and enable predictive maintenance.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions across a network of computers. In the supply chain, blockchain can enhance traceability, provenance, and security. It enables end-to-end visibility, reduces fraud, streamlines supply chain finance, and facilitates secure and efficient digital contracts and payments.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks in the supply chain. It can streamline order processing, data entry, invoice processing, and other administrative tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. RPA improves accuracy, reduces cycle times, and enhances operational efficiency.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms provide scalability, flexibility, and accessibility to supply chain stakeholders. They facilitate real-time collaboration, data sharing, and integration across different systems and organizations. Cloud-based solutions enable centralized data storage, analytics, and application hosting, supporting supply chain visibility, agility, and decision-making.
- Advanced Analytics and Predictive Analytics: Advanced analytics techniques, such as data mining, statistical modeling, and optimization algorithms, help organizations derive insights from complex supply chain data. Predictive analytics leverages historical data and AI/ML algorithms to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, predict maintenance needs, and anticipate supply chain risks and disruptions.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are finding applications in areas like warehouse operations, training, and maintenance. AR overlays digital information onto the real-world environment, providing workers with real-time guidance, visualizations, and instructions. VR can simulate training scenarios and remote collaboration, enhancing safety, efficiency, and knowledge transfer.
- 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing allows the production of customized products on demand and closer to the point of consumption. It reduces lead times, inventory requirements, and transportation costs. Additive manufacturing enables decentralized production, mass customization, and supply chain resiliency.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: As supply chains become more digitized, the importance of cybersecurity and data privacy increases. Protecting sensitive data, securing networks and systems, and ensuring compliance with regulations are critical considerations in supply chain digital transformation.
These tech trends are continuously evolving and are likely to shape the future of supply chain management, enabling organizations to operate more efficiently, responsively, and sustainably.